This 15-storey building is located on top of an underground parking structure. The customer conducted Modal Analysis measurements using ARTeMIS Modal Pro.
Case: Heritage Court Tower, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada

ARTeMIS Modal
The slender design of High-rise Buildings makes these dynamic sensitive to ambient excitation such as wind and micro-tremors as well as strong motion events such as earthquakes. To reduce the effects of ambient excitation tuned damping systems are often used in this type of structure.
ARTeMIS-SHM
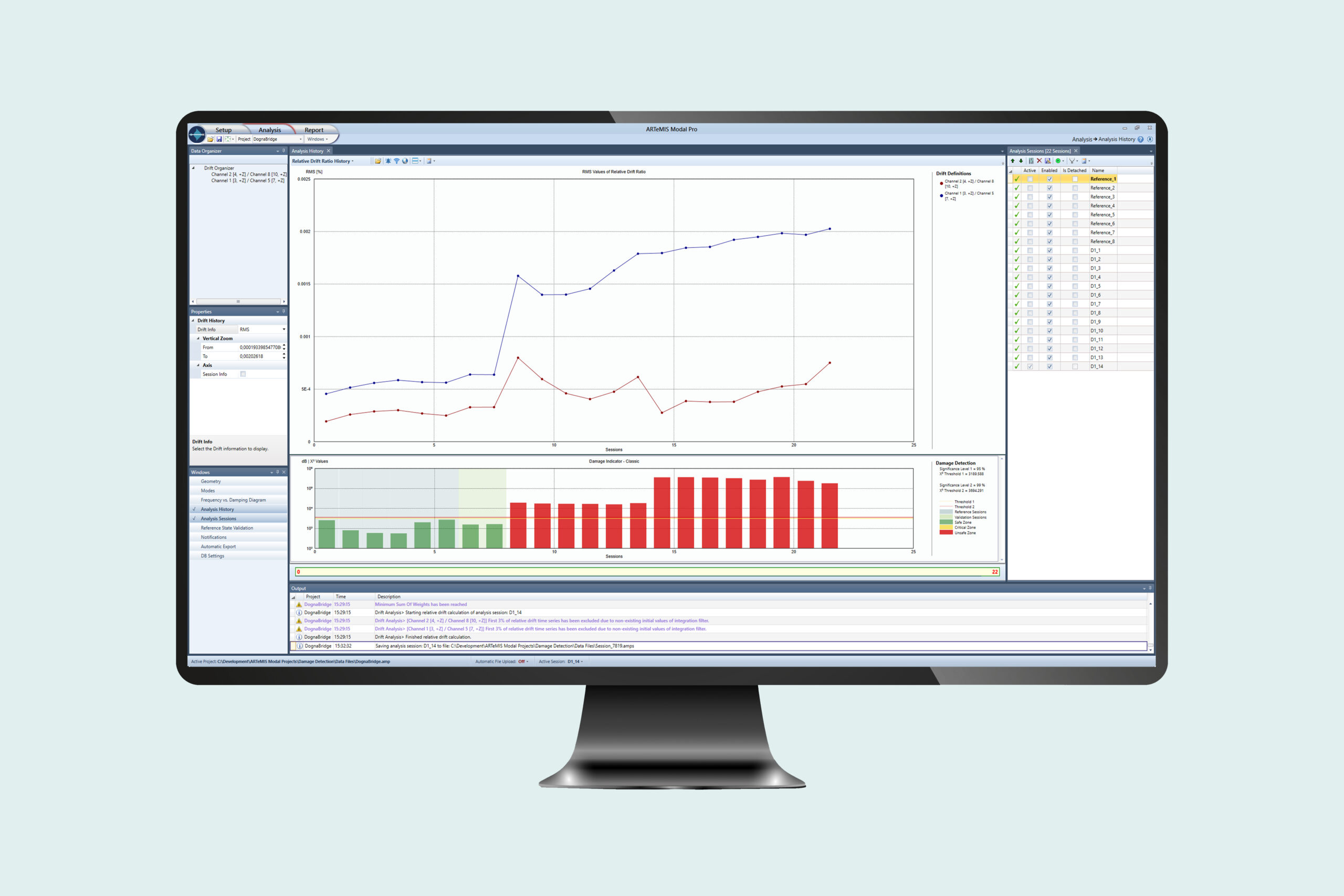
Buildings are designed to stand for many years. However, the health of a structure can deteriorate over years of service due to many reasons. Therefore, continuous monitoring should be undertaken for critical structures in as early a state as possible.
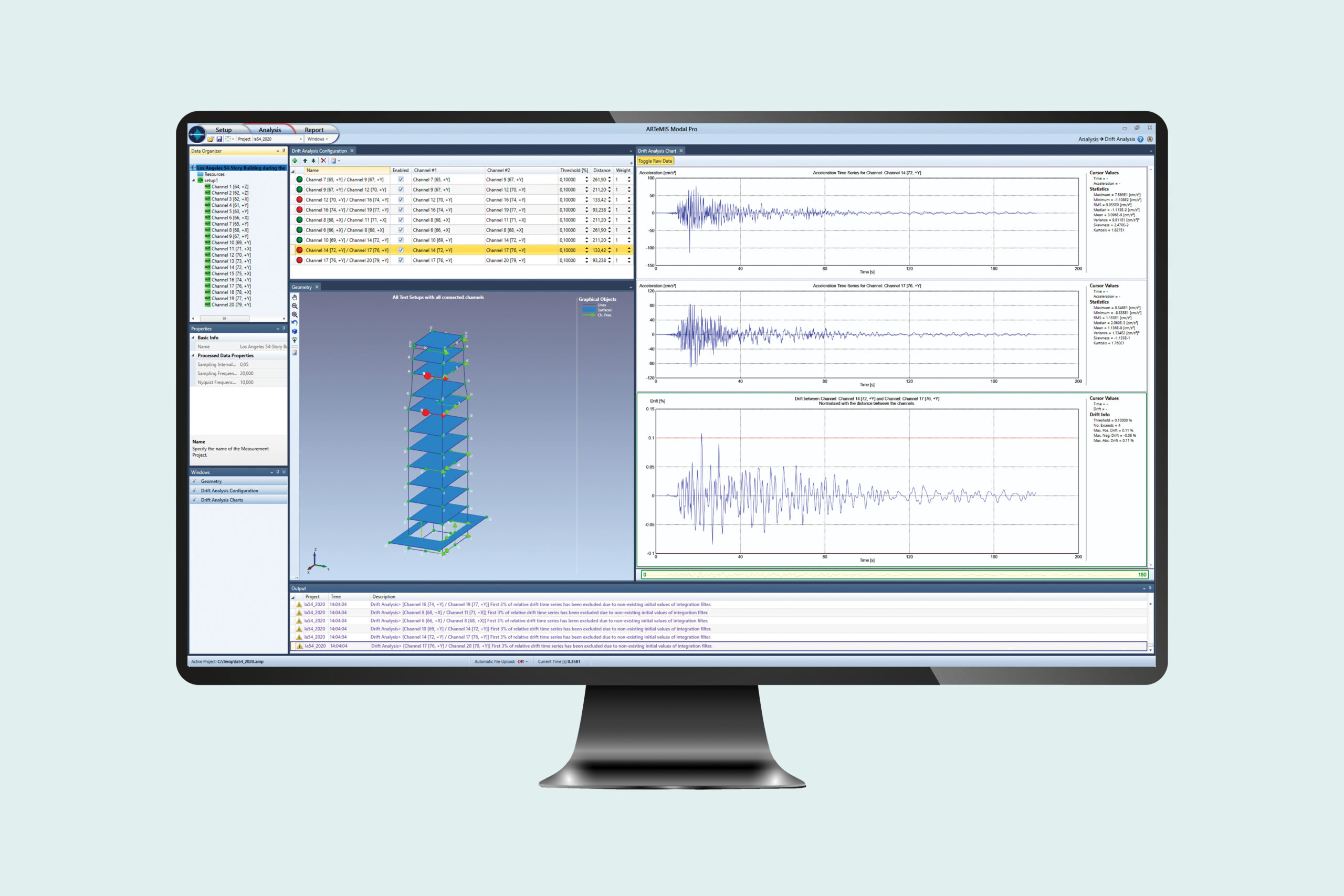
Interstorey Drift Analysis
The Drift Analysis Module is designed to analyze interstorey drift based on measurements from sensors located at the top and bottom of structural elements. These elements can e.g. be columns. If the drift exceeds a certain percentage of the distance between the sensor locations, the module will automatically alert the user.